Tabla de Contenidos
Examen Parcial - 61.08. Álgebra II A - 13 de Mayo de 2006
Cátedra: Incógnita
Fecha: Oportunidad X - 1° Cuatrimestre 2006
Tema: 2
Día: Sábado 13/05/2006
Esta página está incompleta; podés ayudar completando el material.
Enunciado
Punto I
- Sea
 . Pruebe que
. Pruebe que  y que
y que  es producto interno en
es producto interno en  .
. - Dados
 y
y  , hallar todos los
, hallar todos los  tales que
tales que  .
.
Punto II
- Sabiendo que
 es la matriz de proyección sobre cierto subespacio
es la matriz de proyección sobre cierto subespacio  de
de  , hallar las matrices de proyección sobre los subespacios
, hallar las matrices de proyección sobre los subespacios  y
y  .
. - Determinar si la siguiente afirmación es verdadera o falsa:
Si ,
,  y
y  es inversible, entonces
es inversible, entonces  es solución por cuadrados mínimos de
es solución por cuadrados mínimos de  si y sólo si
si y sólo si  es solución por cuadrados mínimos de
es solución por cuadrados mínimos de  .
.
Punto III
- Sea
 . Para
. Para  , definimos
, definimos  mediante
mediante  .
.- Probar que
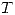 no es biyectiva.
no es biyectiva. - Considerando
 y el PI
y el PI  , hallar todos los
, hallar todos los  tales que
tales que  , con
, con  .
.
Punto IV
- Considere la ecuación diferencial
 .
.- Hallar la solución general de la ecuación homogénea asociada.
- Considerando
 y
y  , hallar todas las soluciones que tengan límite finito cuando
, hallar todas las soluciones que tengan límite finito cuando  .
.
El examen se aprueba resolviendo correctamente cuatro puntos. Justificar todas las respuestas.
Resolución
Discusión
Si ves algo que te parece incorrecto en la resolución y no te animás a cambiarlo, dejá tu comentario acá.
Excepto donde se indique lo contrario, el contenido de esta wiki se autoriza bajo la siguiente licencia: CC Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
